Dividends vs Interest: What’s the Difference?
Dividends are payments made by a company to its shareholders in the form of cash or stock. When a company declares a dividend, it is announcing that it intends to distribute cash to shareholders during the current fiscal year. This notification can serve as an important signal to investors about the financial health of the company.
The amount of a dividend payout will depend on many factors, including the size and performance of the underlying stock market index, corporate governance rules at the issuing company, and prevailing economic conditions. Historically, dividends have been one of the most reliable sources of income for long-term investors.
Dividends are an important part of corporate finance and serve as an important signal to investors about a company’s financial health and future prospects.
Interest income is a category of income that comes from investing via borrowing money. The interest earned on the loan is paid back to the lender over time and is considered an important part of an investor’s revenue stream. Interest income can come from both fixed-income investments, such as bonds, and variable-income investments, such as certificates of deposit (CDs).
Section A: Dividends
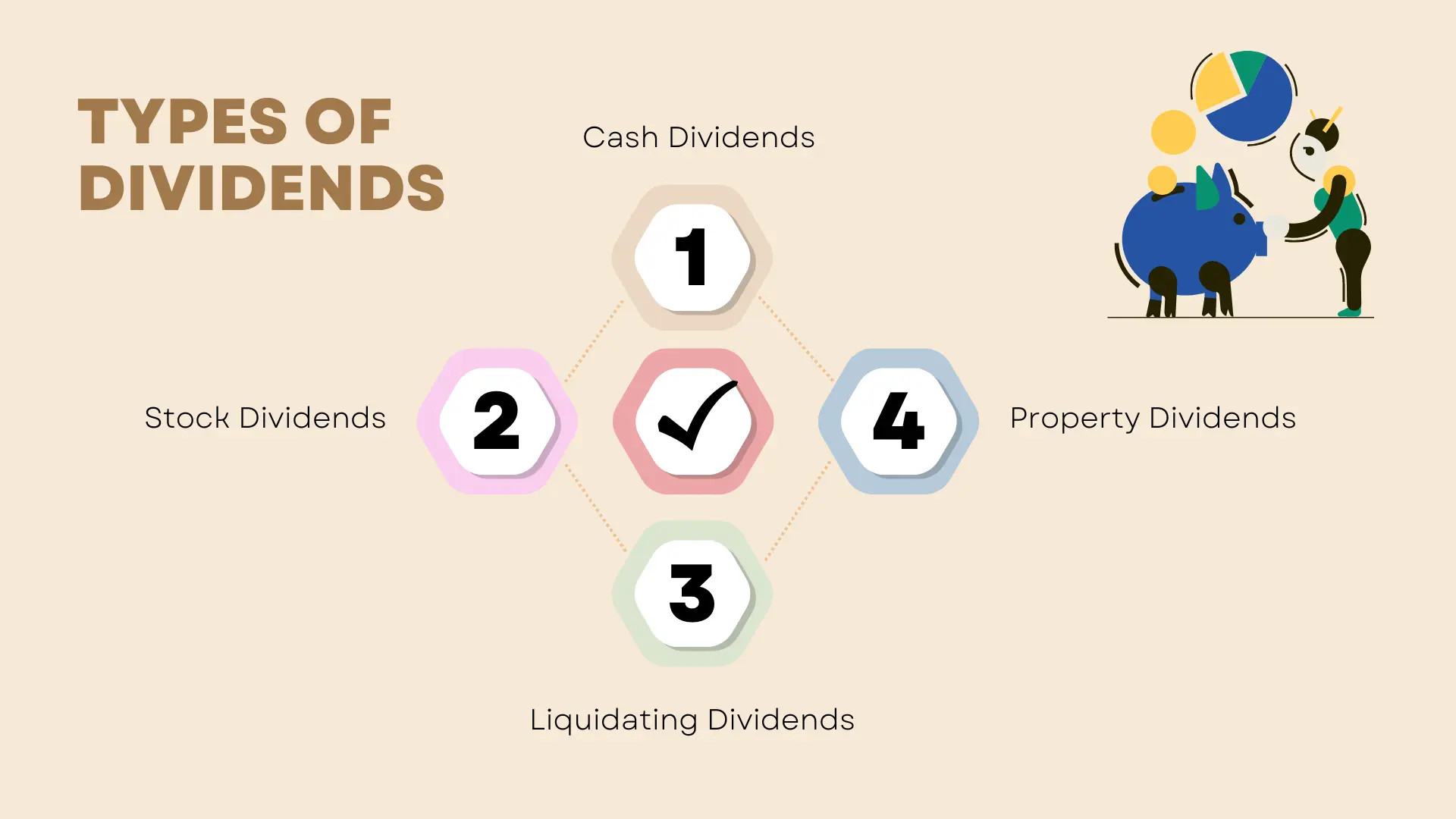
Types of Dividends
a. Cash Dividends
Cash dividends are a way for companies to distribute cash to shareholders. They’re typically paid out in the form of a check or money order, and they’re usually taxable as income.
There are a couple of different types of cash dividends: regular and special. Regular dividends are paid out every quarter, and they account for the vast majority of cash distributions. Special dividends are paid out only when there’s a change in stock prices that results in a corresponding increase or decrease in the company’s net worth.
Cash dividends can be great tools for investors because they offer an easy way to get some extra money (in the form of free money) every quarter. And since they’re typically tax-free, they’re an especially good option if you’re trying to maximize your income taxes.
b. Stock Dividends
Stock dividends are a type of distribution from a company’s shares. They are paid out as a percentage of the outstanding shares on a regular basis. The frequency and amount of stock dividends can vary, but they are usually paid quarterly. Dividends may also be declared in advance, meaning the dividend will be paid out even if the company does not reach its quarterly earnings goal.
Stock dividends can provide investors with important income opportunities. They may also help to increase the value of a company’s stock, since they represent additional compensation for shareholders. In some cases, dividend payments may be contingent upon the company meeting certain financial targets or achieving specific business objectives.
Most investors prefer to receive stock dividends rather than cash distributions in order to maintain ownership of their investments.
c. Property Dividends
Property dividends are a form of property that is given to shareholders of a company as an incentive for holding the stock. The main benefits of property dividends are that they are tax-free, and they provide consistent cash flow to shareholders.
Property dividends are usually declared and paid out at regular intervals, typically every three months or six months. Property dividends are considered both a return of capital to shareholders and an incentive to keep them invested in the company’s shares.
Most property dividends are paid out as units of property, and some companies permit their shareholders to sell these later at a profit. Property dividends provide shareholders with a regular income and help to stabilize share prices over time. They can also provide stability for shareholders during times of market volatility, because property values often increase even if the stock price goes down.
d. Liquidating Dividends
Liquidating dividends are a type of dividend paid to shareholders of a company that is in financial trouble. This happens when the company can no longer afford to pay out regular dividends and instead chooses to distribute all its remaining profits as a lump sum payment to shareholders.
The main reason companies would liquidate their dividends is because they are in debt and need to disburse liabilities and then restructure that debt. Some other reasons include if the company feels it will be profitable again in the future and wants to give its shareholders a return on their investment, or if the board of directors believes there is an opportunity for more growth in the company by selling off assets.
When a company liquidates its dividends, it means that shareholders will not receive any further payments from that company.
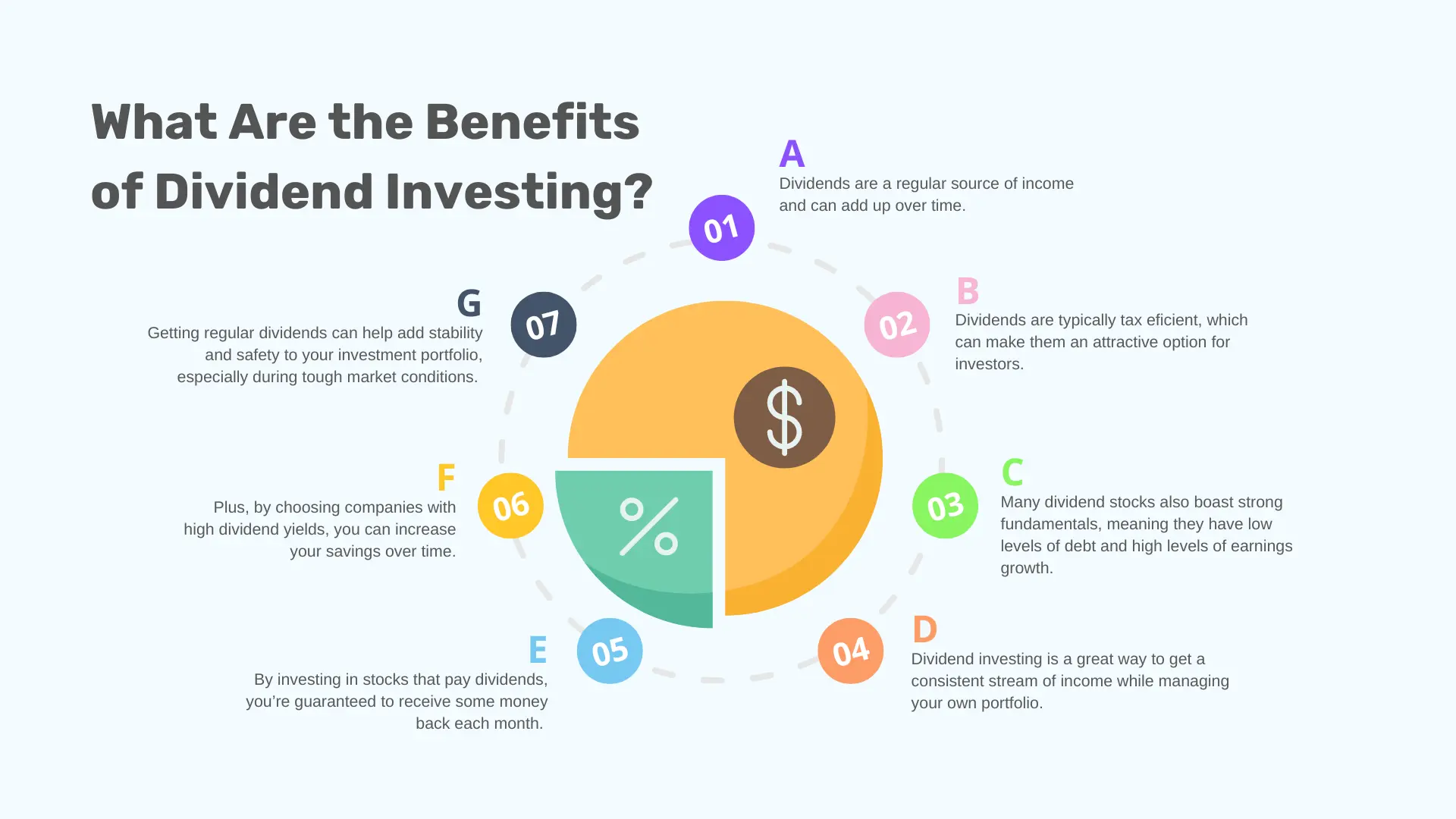
What Are the Benefits of Dividend Investing?
Dividend investing can be a great way to build wealth over time. Here are some of the benefits:
a. Dividends are a regular source of income and can add up over time.
b. Dividends are typically tax efficient, which can make them an attractive option for investors.
c. Many dividend stocks also boast strong fundamentals, meaning they have low levels of debt and high levels of earnings growth.
d. Dividend investing is a great way to get a consistent stream of income while managing your own portfolio.
e. By investing in stocks that pay dividends, you’re guaranteed to receive some money back each month.
f. Plus, by choosing companies with high dividend yields, you can increase your savings over time.
g. Getting regular dividends can help add stability and safety to your investment portfolio, especially during tough market conditions.
How Do You Calculate Dividend Payments?
Dividend payments are an important part of a company’s overall financial statement. There are a few steps that you need to take to calculate dividend payments.
The first step is to determine the company’s profit before taxes (PBT). This can be done by subtracting the costs of goods sold from the total revenue.
Next, you will need to divide PBT by the number of shares outstanding. This will give you the company’s dividend payout ratio.
Finally, you will need to multiply the dividend payout ratio by the share price on the ex-dividend date to get the payment amount in cash or stock.
Section B: Interest Income
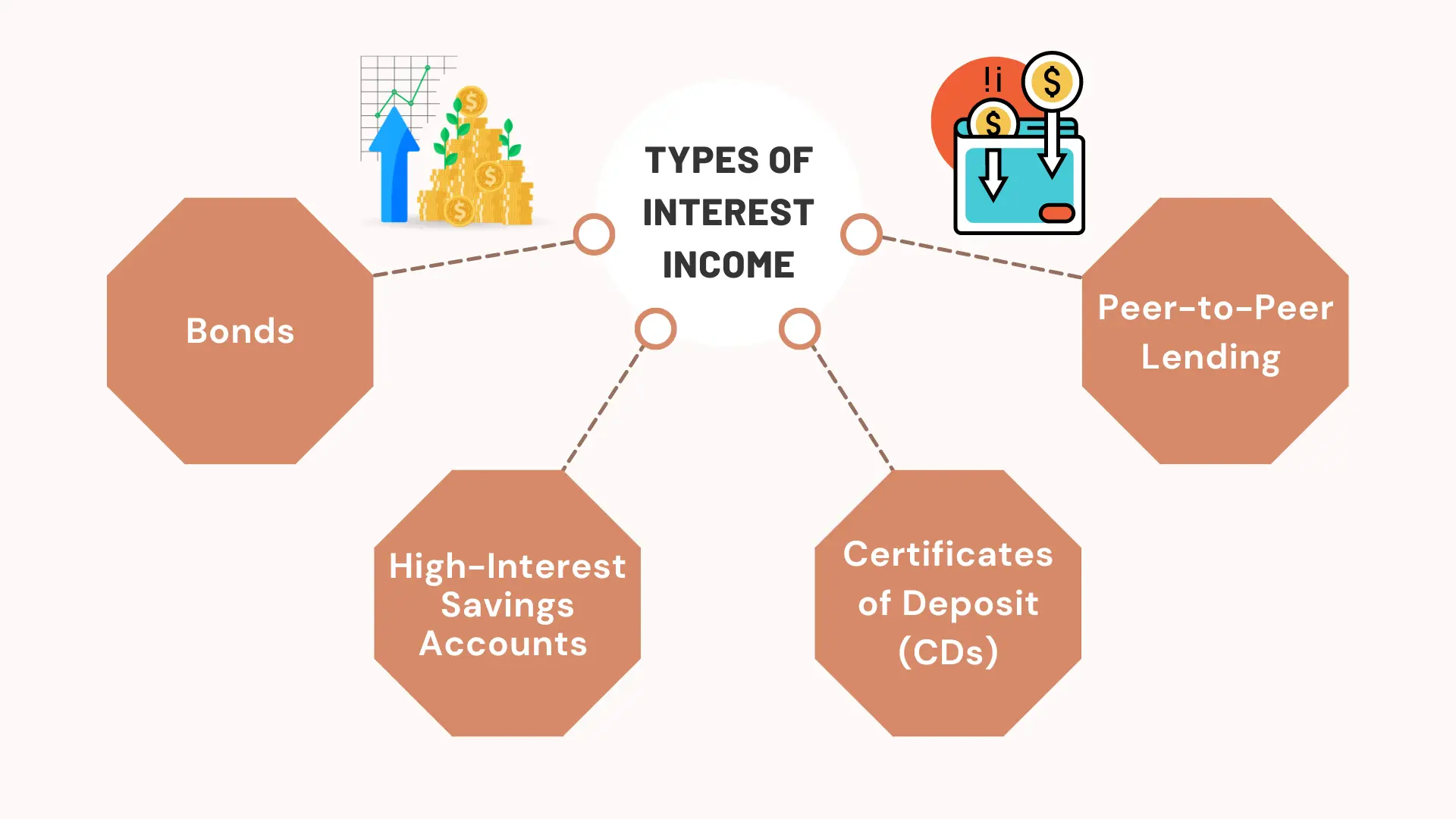
Types of Interest Income
a. Bonds
Bonds are financial instruments that provide a return on investment, typically paying interest payments each month. Bonds are fixed-income securities that generally have a maturity date and offer investors stability in terms of their income.
Investors buy bonds to get a guaranteed return on their money while the issuer promises to make regular interest payments. Bond prices rise and fall with the overall market, but they tend to hold their value over time relative to other investments. When interest rates go up, bond prices fall because their returns decrease; when rates go down, bond prices rise because their returns increase.
Bonds can also be sold short (bet against) or bought long (invest in).
b. High-Interest Savings Accounts
High-Interest Savings Accounts (HISAs) are a type of savings account with higher interest rates than regular savings accounts. HISAs let you save money for longer periods of time, which can help you achieve your financial goals faster. Some factors to consider when opening an HISA include the bank’s available interest rates and how often your deposit will be compounded.
There are a few things to keep in mind when opening an HISA account:
- You should always compare current interest rates online before making a decision.
- Make sure the bank has a good reputation and is FDIC insured.
- Make sure to sign up for automatic interest withdrawals so that your profits will be automatically deposited into a separate account each month.
c. Certificates of Deposit (CDs)
Certificates of deposit are a type of savings account that offer higher returns than other types of bank accounts. A CD has a fixed term, typically 6 months to 2 years, and you are guaranteed the interest rate on the account at the time you open it. You can also often withdraw money from your CD early without penalty, although there may be a fee associated with this.
CDs are a good option for those who want to secure a high return on their deposited money but don’t want to risk losing all their money if something unexpected happens. Additionally, CD rates tend to be stable over time, which can make them an attractive option for long-term savings.
d. Peer-to-Peer Lending
Peer-to-peer lending is a new form of borrowing that uses networks of borrowers and lenders to make and deliver loans. With peer-to-peer lending, you don’t need to go through a bank or other traditional lender. Instead, you can borrow money from your friends and acquaintances. This makes peer-to-peer lending a convenient and affordable way to give and get loans.
Peer-to-peer lending is also different than other forms of borrowing because it doesn’t require you to collateralize your loan. This means that you don’t have to put up property or other valuable assets as security for the loan.
One downside of peer-to-peer lending is that it’s not regulated by the banking system like traditional lenders are. This can lead to risky investments for lenders, as it can be difficult to find reliable borrowers in the market.
What Are the Benefits of Interest Income Investing?
Interest income investing can offer a number of benefits for individuals, couples, and families.
For individuals, interest income can provide an additional source of income. Additionally, interest income can be used to cover expenses such as rent, groceries, and utilities. Some investors also use interest income to make additional investments or to save for future goals.
Couples may find that interest income helps them save money on their overall budget. Additionally, couples may use interest income to cover unexpected expenses or to pay down debt. Finally, couples may use interest income to invest in mutual funds or other types of vehicles that offer higher returns than traditional savings accounts.
For families, interest income investing can help reduce the amount of financial stress that is experienced every month. Additionally, families may find that interest income provides a stable source of income that is not subject to market fluctuations.
How Do You Calculate Interest Income?
Interest income can be calculated in a variety of ways. The simplest way to calculate interest is to use the interest rate on a fixed-income security as the underlying calculation. For example, if you have a $100,000 investment that pays 6% interest, your annual interest income would be $600.
Alternatively, you could calculate interest by multiplying the principal amount of the investment by the applicable interest rate. For example, if you have a $100,000 investment that pays 10% annual interest, your annual interest income would be $1,000.
You could also calculate total periodic interest payments by adding all of the monthly or quarterly installment payments together and dividing that sum by 12. This method is typically used when calculating mortgage or loan payments.
you can find a great interest calculator here
The Bottom Line: Which Is Better?
Both types of income are important for long-term financial stability. However, when comparing dividend income to interest income, it is often advantageous to choose dividend income. This is because dividends are taxed at a lower rate than interest income payments. Additionally, the stock market typically trends upwards over time, which increases the potential returns on invested money.
Conversely, when comparing interest income to other sources of income, such as wages or salary, it may be more beneficial to take invest excess funds in a higher-yielding investment such as bonds or certificates of deposit. This is because interest payments are able to provide predictable monthly incomes.
Ultimately, the best way to determine whether dividend or interest income is better for you depends on your individual situation and financial goals.